Knowing who your competitors are and how they affect your business is very important for you to succeed. Whether you’re a large company or a small one, competition is a big factor in determining your performance. One useful tool to evaluate your competition and understand your position in the industry is Porter’s Five Forces model.
This blog post will provide a detailed explanation of Porter’s Five Forces model.
What is Porter’s Five Forces model?
Porter’s Five Forces model is a tool used to analyze competition in business. It looks at factors that affect how profitable a business is compared to others in the industry. This model, created by Michael E. Porter in 1979, helps you understand your industry better and make strategic decisions to succeed in a competitive market. By using this model along with other tools, you can gain valuable insights and stay ahead in business. Understanding Porter’s Five Forces can give you an advantage in the business world.
Porter’s Five Forces are basically useful to analyze the following information:
- The risk of new competitors entering the market.
- The danger of substitute products or services
- The influence that customers have in negotiating with businesses.
- The influence that suppliers have in negotiations.
- The level of competition between businesses is known as the intensity of competitive rivalry. It refers to how fierce and strong the competition is in a particular industry.
Michael Porter’s Five Forces model is a helpful tool for assessing how competitive your company is. It might seem complex at first, but the main concepts are actually pretty straightforward. The five forces that can impact your company’s success and profits are the risk of new competition, supplier power, buyer bargaining power, the threat of substitute products, and rivalry among competitors. To outperform your competition and stay strong in the market, it’s crucial to grasp these factors and how they connect. So, I recommend any business owner aiming for success dive into understanding Porter’s Five Forces.
Understanding Porter’s Five Forces
If you want to beat your competition, it’s helpful to know about Porter’s Five Forces model. This model helps you study your industry and rivals so you can be ready to make the most of market chances and challenges. By understanding your industry and keeping up with the latest news, you can use this model to get ahead of your competitors. Michael Porter’s Five Forces is a useful method for checking the industry’s condition and knowing the competitive environment. By using this model, you can see how these forces affect your industry and find ways to do better than your competitors.
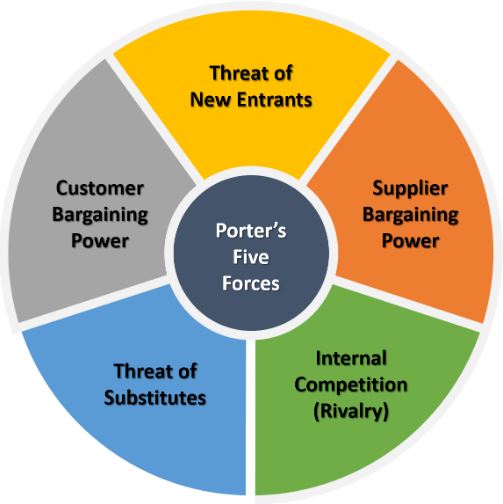
The Five Forces model looks at five important factors that impact how competitive an industry is. These factors are:
1. Competitive Rivalry
The first of Porter’s Five Forces is about competitive rivalry, which is a fancy way of saying competition between businesses. Think about Pepsi and Coke, Apple and Samsung, Nike and Adidas. These companies are always trying to outdo each other to win over customers. The more competitors you have and the better their products are, the harder it is for you to stand out. In a crowded market, companies lower prices and advertise a lot to get noticed. But if you’re in a unique position with few rivals, you can charge more and make more money.
2. Potential for New Entrants in an Industry
In industries where it’s easy for new companies to start up, like local restaurants, the profit margins are typically lower, and each company has a smaller share of the market. This means that your favorite restaurant might not last long because of tough competition and the constant arrival of new dining spots. The Threat of New Entrants is one of the factors in Porter’s Five Forces analysis, which looks at how new competitors could affect existing businesses in an industry. This analysis helps us understand how competitive an industry is and how attractive it may be for new businesses. Michael Porter, a professor at Harvard University, developed this framework, which also includes factors like competitive rivalry, buyer power, substitutes, and supplier power.
3. Supplier Power
Supplier Power refers to the influence that suppliers have on a business. Suppliers have power if they can easily raise prices or lower the quality of their products. If you rely on one supplier for something you need, they have a lot of power over your business. It can be costly to switch to a different supplier. Having more supplier options makes it easier to switch to a cheaper one. But if you have fewer options and rely heavily on a supplier, they can charge you more. This can affect your profits if you’re stuck with expensive contracts.
4. Customer or buyer Power
When customers have more influence, they can push businesses to offer better products or services at lower prices. This influence becomes stronger when there are fewer buyers compared to suppliers in an industry, giving customers more leverage. This is known as “buyer power,” and it means customers can easily switch to cheaper alternatives, putting pressure on prices.
Consider the number of customers you have, how much they buy, and the ease with which they could switch to a different seller. If you have only a few knowledgeable customers, they hold more power. On the other hand, if you have many customers and little competition, buyer power decreases.
5. Threat of Substitutes
When customers can easily find other options similar to the services provided by a particular industry, it poses a significant threat to companies within that industry. This threat is higher when customers can easily switch to a different product that is cheaper or better, or when a new and desirable product is introduced unexpectedly into the market.
Conclusion
Understanding Porter’s Five Forces model can provide businesses with valuable strategic insight into their industry. By analyzing the forces of competition, suppliers, customers, new entrants, and substitutes, companies can make informed decisions to gain a competitive advantage. Mastering this framework allows organizations to develop effective strategies to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities in the market.